Sign-In or Create an Account to find your purchasing solution
Become a registered Edgetech partner to start using our latest insulating technology in your glazing systems.
Tel: +44 02476 639931
Email: ukenquiries@edgetechig.com
Orders: ukorders@edgetechig.com
Improving the energy efficiency of insulating glass units (IGUs) is a priority for window manufacturers, specifiers and building owners. One component that has a significant influence on performance is the thermal spacer bar, which can improve U‑Values by up to 0.2 W/m²K when advanced warm edge technology is used instead of traditional alternatives.

Windows are a major route for heat loss in any building, so the construction of the sealed unit has a direct impact on comfort and energy use. The spacer bar that separates the panes plays a key role by helping to control heat transfer at the edge of the glass and the conditions inside the cavity.
By reducing thermal bridging and managing moisture, modern spacer systems help enhance the overall thermal performance of the unit and support higher Window Energy Ratings. This also assists in reducing condensation risk around the perimeter of the glass.
View our product range
A thermal spacer bar is the continuous component that separates the panes of glass in an IGU and forms part of the edge seal. It defines the cavity width, incorporates desiccant to adsorb moisture and provides a surface for primary and secondary sealants to bond to.
In double glazing, a single spacer bar separates the two panes to create one insulating cavity. In triple glazing, two spacer bars create two cavities, which increases the potential for thermal enhancement while also placing greater importance on the performance of the spacer system.
Historically, aluminium spacer bars were widely used because they are strong and easy to process. However, aluminium is a highly conductive material and forms a thermal bridge at the edge of the unit, increasing heat loss and the likelihood of condensation.
Warm edge spacer technology was developed to address this issue by replacing metal with low‑conductivity materials. These systems use structural foam or composite constructions to provide a “warm edge” where internal surface temperatures are higher compared with traditional aluminium spacers.
Reducing the conductivity at the edge of the glass helps limit the transfer of heat from inside to outside. This in turn can improve the overall U‑Value of the window and helps maintain more comfortable temperatures near the glass.
Warm edge spacers also contribute to reducing the risk of condensation around the perimeter because the internal glass edge temperature is higher than it would be with traditional aluminium spacers. By combining lower thermal conductivity with effective moisture control, modern warm edge systems support both energy efficiency and durability.

Different spacer types offer varying levels of performance in terms of thermal conductivity, moisture management and long‑term seal integrity.
| Spacer type | Thermal behaviour and U‑Values | Desiccant and moisture control | Primary seal and durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium spacer | High thermal conductivity, creating a thermal bridge that increases heat loss at the glass edge. | Limited moisture capacity compared with advanced solutions. | Rigid metal can place more stress on seals under temperature changes. |
| Standard warm edge spacer | Lower conductivity than aluminium, helping to reduce edge heat loss. | Improved desiccant use compared with traditional metal spacer systems. | Typically designed to enhance seal adhesion and reduce stress versus metal. |
| Super Spacer® | Structural foam system that is 950 times less conductive than traditional aluminium spacers, enabling U‑Value reductions of up to 0.2 W/m²K. | Integrated desiccant within the foam to help control moisture inside the cavity. | Flexible multi‑component construction to support long‑term seal performance and gas retention. |
This progression from metal to warm edge foam spacers underpins the improved thermal performance available from modern IGUs
Condensation at the glass edge can be both unsightly and a potential contributor to issues such as mould growth and damage to surrounding materials. By maintaining higher internal surface temperatures at the perimeter, warm edge spacer systems help reduce the conditions in which condensation forms.
Effective desiccant performance inside the spacer also helps control moisture within the cavity itself, supporting the long‑term clarity and durability of the unit. This combination of thermal and moisture management is an important part of delivering reliable, long‑life IGUs.
In triple glazed units, the spacer bar has an even more important role to play. Two cavities provide additional thermal and acoustic benefits, but they also require the spacer system to maintain performance across a larger edge area.
Warm edge spacers used in triple glazing must accommodate movement, support gas retention and continue to limit thermal bridging at multiple edges. When specified correctly, they can help triple glazed units achieve very low U‑Values and contribute to a comfortable internal environment.
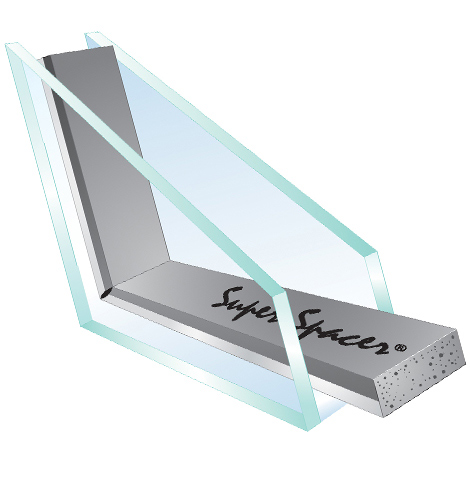
Super Spacer® was introduced in 1989 and is recognised as the first flexible foam warm edge spacer system. Since then, it has been used in many types of buildings around the world and remains a leading warm edge solution.
The structural foam construction of Super Spacer® delivers very low thermal conductivity and excellent UV resistance. Its integrated desiccant and flexible design support long service life, energy efficiency and reduced condensation risk.
By being 950 times less conductive than traditional aluminium spacer bars, Super Spacer® can improve the energy performance of windows by up to 0.2 W/m²K and help them achieve maximum Window Energy Ratings. This makes it well suited to both residential and commercial applications where energy efficiency is a priority.
For projects with higher structural or performance demands, TriSeal™ offers a purpose‑designed triple‑seal configuration. It is particularly well suited to commercial and structural glazing applications.
TriSeal™ combines three key elements: an inner acrylic adhesive for initial strength and handling, a polyisobutylene primary seal to help retain gas within the unit, and an outer silicone seal to provide robust structural performance. Together, this triple‑seal design supports long‑term durability while delivering the benefits of warm edge technology.

Thermal spacer bars are a relatively small part of the IGU, but their impact on overall performance is significant. Moving from traditional aluminium spacers to warm edge solutions such as Super Spacer® and TriSeal™ helps improve U‑Values, reduce condensation risk and support the creation of more energy‑efficient buildings.
To learn more about how these technologies can support your glazing projects, or to see how warm edge science is applied in commercial and other sectors, contact Edgetech or explore the relevant sector pages on the Edgetech website.
As energy costs rise and concerns for the environment grow, it’s important to invest in the highest quality thermal spacer bars for sustainable building design. Contact our friendly team and start using Edgetech technology today.
Please fill out the form below to a find a local supplier. Once we've found you closest suppliers you will be able to contact them all.
Your enquiry has been successfully submitted. You should receive an email or callback with 24-48 hours.
Return to the homepage